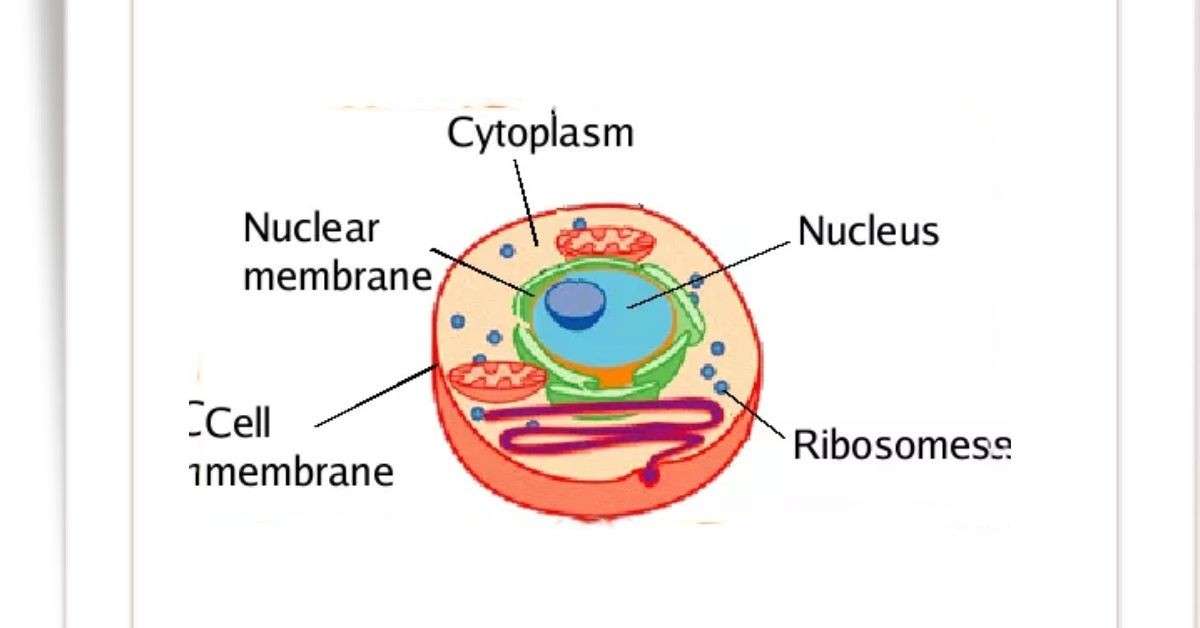
Drawing Of Ribosomes
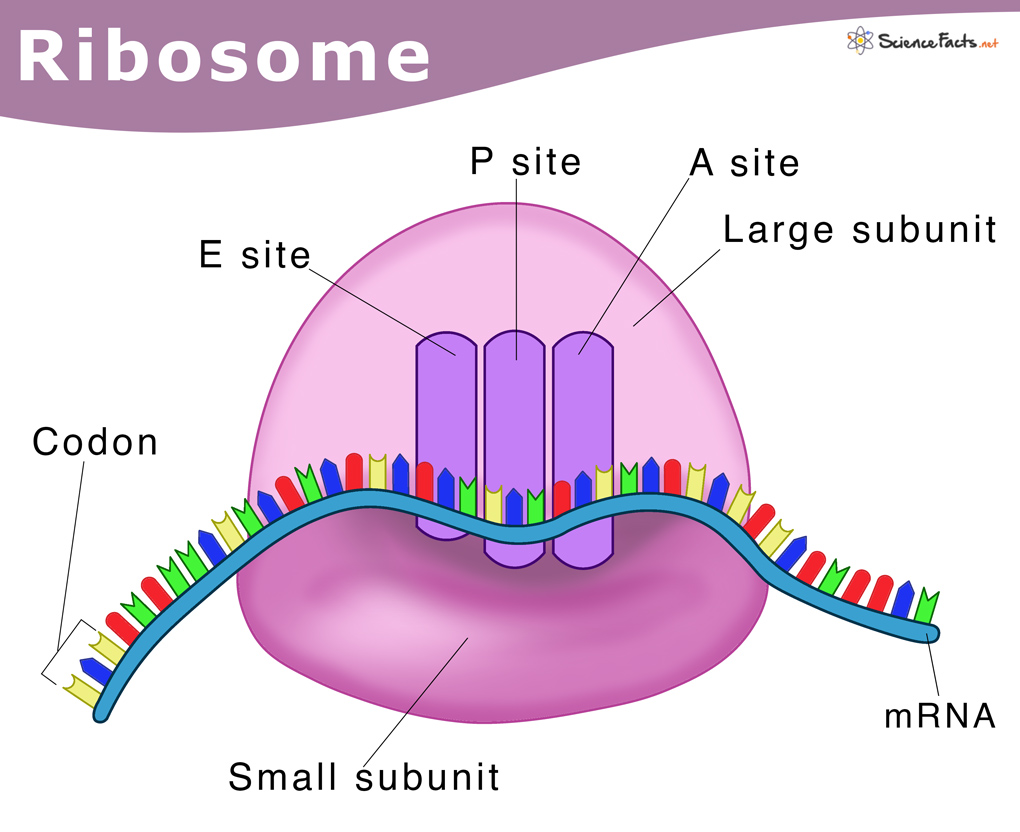
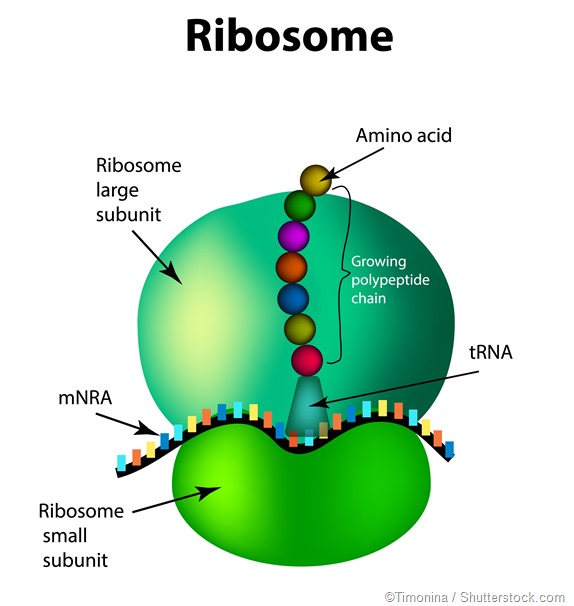
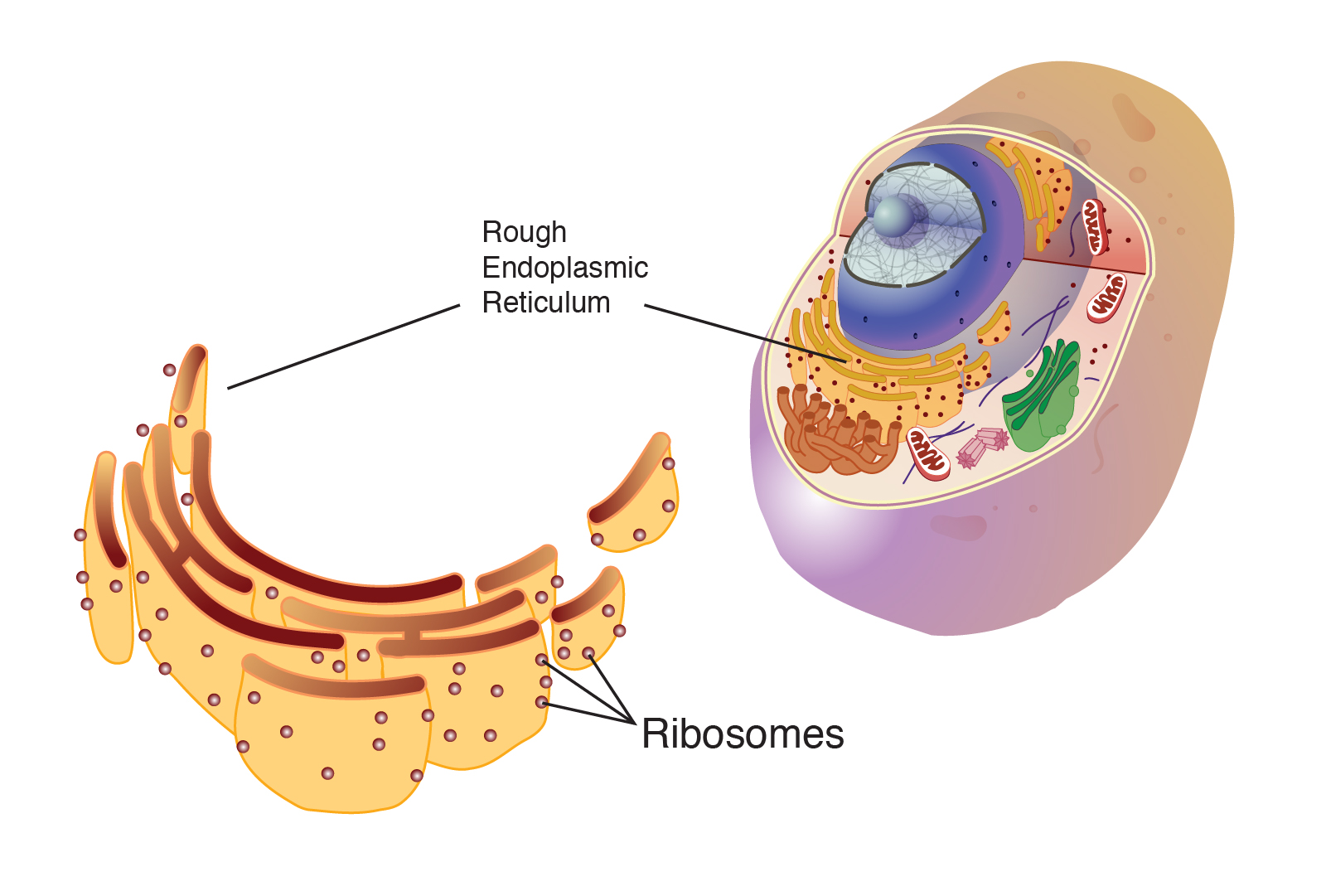
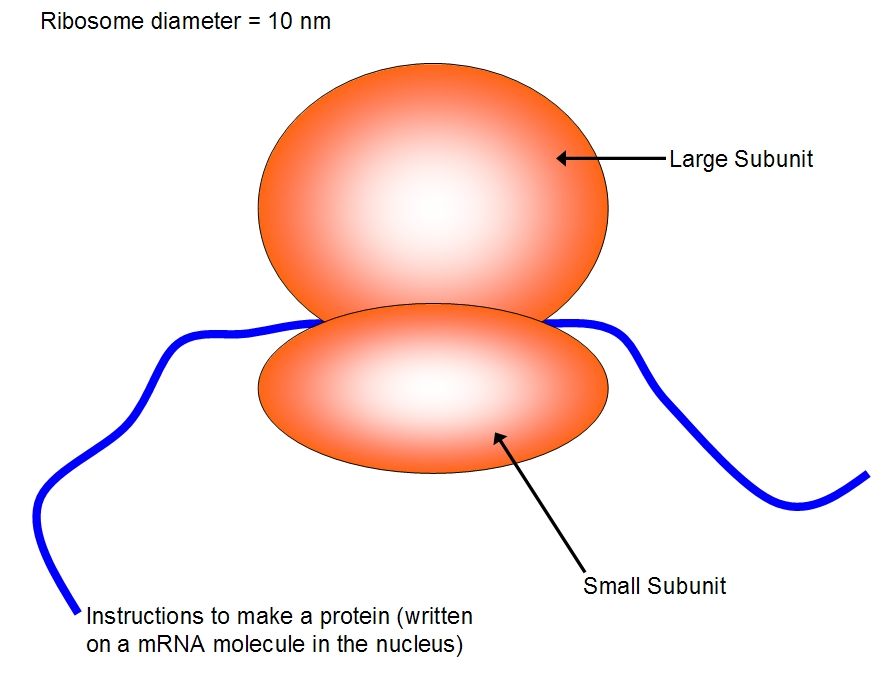
Drawing Of Ribosomes - In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is completely specialized for the synthesis and assembly of rrnas. Long chains of amino acids fold and function as proteins in cells. These structures are comprised of two major. Facts, analogy, meaning, components, structure, & purpose with examples, & labeled picture. Web a ribosome is a complex cellular mechanism used to translate genetic code into chains of amino acids. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. Cells contain parts called organelles. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. A smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mrna pattern, and The process of protein synthesis is a primary function, which is performed by all living cells. Web how do you make a ribosome? Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: Web ribosomes can be found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Web a ribosome is a complex macromolecule composed of structural and catalytic rrnas, and many distinct polypeptides. A large and a small subunit. The tinier subunit is the place the mrna binds and it decodes, whereas the bigger subunit is the place the amino acids are included. In the nucleolus, new ribosomal rna combines with. Follow me step by step to draw it very easily with me. Cells contain parts called organelles. Web ribosomes | structure of ribosomes | easy step by step diagram of ribosomes | class 9th | biology. Web a ribosome is a complex cellular mechanism used to translate genetic code into chains of amino acids. The small and large ribosomal subunits. Web structure of ribosomes. A smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mrna pattern, and Web in this video i'm going to draw diagram of the ribosome, please send your feedback, #ribosome #ribosomediagram. So friends of you have problem in any other thing so tell me. Web ribosomes receive their “orders” for protein synthesis from the nucleus where the dna is transcribed into messenger rna (mrna). Ribosomal molecules of messenger rna (mrna) determine the order of transfer rna (trna) molecules that. Web ribosomes collect and link amino acids together. Web in this video. Every set of 3 nucleotides (called a codon) contains the blueprint for a specific amino acid. Ribosomes, not the mrna itself, pair with the mrna in the cytoplasm. A smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mrna pattern, and All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls. Mrna is a chain of chemicals called nucleotides, which a ribosome “reads” in groups of three: These structures are comprised of two major. In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is completely specialized for the synthesis and assembly of rrnas. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Long. The function of a ribosome in any cell is to produce proteins. In this video, you will learn how to draw. Mrna is a chain of chemicals called nucleotides, which a ribosome “reads” in groups of three: Ribosomes, not the mrna itself, pair with the mrna in the cytoplasm. Ribosomal molecules of messenger rna (mrna) determine the order of transfer. Web how do you make a ribosome? These structures are comprised of two major. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. It's an educational video from 9th biology ptb. Web a ribosome is a complex macromolecule composed of structural and catalytic rrnas, and many distinct polypeptides. The ribosome moves forward on the mrna, codon by codon, as it is read and translated into a polypeptide (protein chain). A smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mrna pattern, and Web in this video you will learn a very easy method to draw diagram of ribosomes. Web a ribosome is made up of two basic. Web a ribosome is made up of two basic pieces: The function of a ribosome in any cell is to produce proteins. Web ribosomes are made of proteins and ribonucleic acid (abbreviated as rna), in almost equal amounts. In this video, you will learn how to draw. The process of protein synthesis is a primary function, which is performed by. Web a ribosome is a complex molecular machine found inside the living cells that produce proteins from amino acids during a process called protein synthesis or translation. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose.. During translation, the two subunits come together around a mrna molecule, forming a complete ribosome. It comprises of two sections, known as subunits. In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is completely specialized for the synthesis and assembly of rrnas. The small and large ribosomal subunits. These structures are comprised of two major. The mrna travels to the ribosomes, which translate the code provided by the sequence of the nitrogenous bases in the mrna into a specific order of amino acids in a protein. Some chromosomes have sections of dna that encode ribosomal rna, a type of structural rna that combines with proteins to make the ribosome. Web ribosomes collect and link amino acids together. Cells contain parts called organelles. Web ribosomes are made of proteins and ribonucleic acid (abbreviated as rna), in almost equal amounts. Web structure of ribosomes. A eukaryotic ribosome is composed of nucleic acids and about 80 proteins and has a molecular mass of about 4,200,000 da. It's an educational video from 9th biology ptb. Around 37 to 62% of rna is comprised of rna and the rest is proteins. Web ribosomes are the sites at which information carried in the genetic code is converted into protein molecules. A ribosome is made from complexes of rnas and proteins and is, therefore, a ribonucleoprotein. The ribosome moves forward on the mrna, codon by codon, as it is read and translated into a polypeptide (protein chain). Web ribosomes can be found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. The process of translation occurs on the ribosomes, where the mrna's genetic code is read, and amino acids are assembled into a polypeptide chain to form a protein. Their main function is to convert genetic code into an amino acid sequence and to build protein polymers from amino acid monomers. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits:Ribosomes Definition, Structure, & Functions, with Diagram
The structure of the ribosome Functions Royalty Free Vector
Ribosome Structure
Ribosomes function for kids
The structure of the ribosome Infographics on Vector Image
how to draw ribosome diagram easily YouTube
Ribosome
Ribosomes
Ribosome Structure & Function MCAT Biology MedSchoolCoach
Ribosome Types, Structure and Functions Biology Educare
A Smaller Subunit Which Binds To A Larger Subunit And The Mrna Pattern, And
The Ring Contains One Oxygen And Four Carbons.
Ribosomes Exist In The Cytoplasm In Prokaryotes And In The Cytoplasm And Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum In Eukaryotes.
The Sugar In All Four Nucleotides Is Called Deoxyribose.
Related Post: